Components of the Universe
- kevinjacob0607
- Mar 31, 2024
- 2 min read
Components of the Universe
The universe is everything. Everyone knows about it. The Earth, the Solar System, and the galaxy are all part of the universe. This is well known. But, what are the main fundamental parts of the universe? What do they mean? How much of each is there in the universe? In this article, you will find the answers to these questions and more.
The main fundamental parts of the universe are very broadly classified into normal matter and energy, dark matter, and dark energy. The ratios of these substances that make up the universe is shocking. Dark energy, the largest, constitutes a whopping 69% of the total universe, a lot more than half. The second one, Dark matter, constitutes a comparatively small percentage: 26%. It is not nearly as big as dark energy, but is quite a lot in comparison to the third constituent: normal matter and normal energy. It constitutes only 5% of the universe. This includes everything we can see, touch, and perceive with our senses.
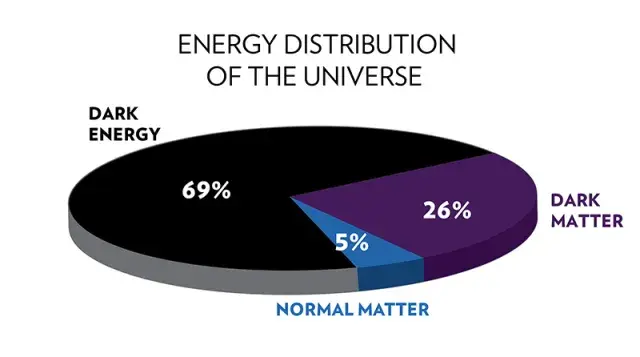
Matter consists only 5% of the universe, but is not very big. Matter occupies space, contains mass and can be perceived by our senses. Heat and electricity are not matter as they do not have mass or occupy space. This means everything we know is matter: Cars, people, planets, stars, everything that is important to us is matter, a part in that 5% of the universe. This brings us to the second component of the universe that we know of: dark matter.
Dark matter is mysterious. Since we do not know much about it, it is nicknamed ‘Dark’ matter. It does not interact with anything, which makes it hard to spot. Therefore, it cannot absorb, reflect or emit any form of light rays, which means it is the closest one can get to being invisible. It has a big gravitational effect on normal matter, which makes it the only reason why scientists know it exists. For galaxy's example, the stars in a galaxy all orbit the black hole in the middle. Black holes make up 0.001% of the galaxies mass, which means the stars in a galaxy are not attracted to the black hole by gravity, but by an invisible and undetectable force. (Home | Cern)
Dark energy is the complete opposite of dark matter. Back in the 1900s, when scientists found out that the universe was expanding, they didn’t know why. They realized that an anti-gravity force that must be filling the fabric of spacetime. They presumed the normal gravity force, along with dark matter, would win eventually. Today, we know the truth. 68% of the universe is dark matter, and scientists estimate that dark matter will eventually win the fight. They speculate that the universe could end by dark energy ripping things apart atom by atom.
Although this might happen, we have nothing to worry about. If this happens, it will happen billions or maybe even trillions of years in the future. Right now, nothing dangerous related to dark matter and dark energy could ever harm us.
Sources used-
Home | Cern- Dark matter
Space.com- Dark energy
Was this useful?
Yes
No
Slightly



Comments